Roles and Permissions
COSMOS Enterprise provides a comprehensive role-based access control (RBAC) system that allows you to manage user permissions across different scopes. This system integrates with Keycloak for authentication and authorization.
Overview
Roles in COSMOS Enterprise control what actions users can perform within the system. Roles are assigned to users per scope, allowing fine-grained control over access to different missions or projects.
Role Naming Convention
Roles are assigned using the format: {SCOPE}__{ROLE_NAME}
SCOPE: The scope name (e.g.,DEFAULT) orALLSCOPESfor global permissionsROLE_NAME: One of the built-in roles or a custom role name
Examples:
DEFAULT__operator- Operator role in the DEFAULT scopeMISSION1__viewer- Viewer role in the MISSION1 scopeALLSCOPES__admin- Admin role across all scopes
Built-in Roles
Individual built-in roles in COSMOS Enterprise are scoped to a minimal set of permissions. Individual users can have multiple roles (e.g., Admin and Operator) if users need administrative access and commanding access. COSMOS Enterprise includes five built-in roles with predefined permission sets:
Admin
The Admin role provides administrative access within a scope. Admins can also manage the files within Bucket Explorer.
Permissions:
system- View system informationsystem_set- Modify system settingstlm- View telemetry datacmd_info- View command informationscript_view- View scriptsadmin- Administrative functions (manage plugins, targets, interfaces, etc.)
Special Cases:
- When assigned to
ALLSCOPES, gainssuperadminpermission for system-wide administration - Can release command authority taken by other users in their scope
Use Case: Users responsible for system configuration and management.
Operator
The Operator role has full access except for administrative functions and approval rights.
Permissions:
system- View system informationsystem_set- Modify system settingstlm- View telemetry datatlm_set- Modify telemetry settingscmd_info- View command informationcmd_raw- Send raw commandscmd- Send commandsscript_view- View scriptsscript_edit- Create and edit scriptsscript_run- Run scripts
Use Case: Power users who need full operational control but not administrative access.
Viewer
The Viewer role provides read-only access to the system.
Permissions:
system- View system informationtlm- View telemetry datacmd_info- View command informationscript_view- View scripts
Use Case: Users who need to monitor telemetry and system status without making changes.
Approver
The Approver role is specifically for command approval workflows.
Permissions:
approve_hazardous- Approve hazardous commandsapprove_restricted- Approve restricted commandsapprove_normal- Approve normal commands
Use Case: Users responsible for reviewing and approving commands before execution.
Runner
The Runner role allows users to execute commands and scripts but cannot create or edit them. Runner does not come with approval rights.
Permissions:
system- View system informationsystem_set- Modify system settingstlm- View telemetry datatlm_set- Modify telemetry settingscmd_info- View command informationcmd_raw- Send raw commandscmd- Send commandsscript_view- View scriptsscript_run- Run scripts
Use Case: Operators who execute procedures and send commands but don't modify configurations or scripts.
Permission Definitions
System Permissions
- system - View system information and status
- system_set - Modify system settings and configurations
Telemetry Permissions
- tlm - View telemetry data
- tlm_set - Modify telemetry settings (limits, conversions, etc.)
Command Permissions
- cmd_info - View command definitions and parameters
- cmd_raw - Send raw binary commands
- cmd - Send commands to targets
Script Permissions
- script_view - View script contents
- script_edit - Create, edit, and delete scripts
- script_run - Execute scripts
Administrative Permissions
- admin - Manage scope-level resources (targets, plugins, interfaces, routers, etc.)
- superadmin - System-wide administration across all scopes (requires
ALLSCOPES__admin)
Approval Permissions
- approve_hazardous - Approve hazardous commands
- approve_restricted - Approve restricted commands
- approve_normal - Approve normal commands
Command Authority
When command authority is enabled for a scope, an additional layer of authorization is applied to command-related permissions:
- Users must "take" command authority for a specific target before sending commands
- Only the user who holds command authority can send commands to that target
- Admin users (with
ALLSCOPES__adminor{SCOPE}__admin) can release authority taken by other users - Command authority applies to these permissions when executed manually:
tlm_setcmd_rawcmdscript_run
Custom Roles
In addition to the built-in roles, you can create custom roles with specific permission combinations.
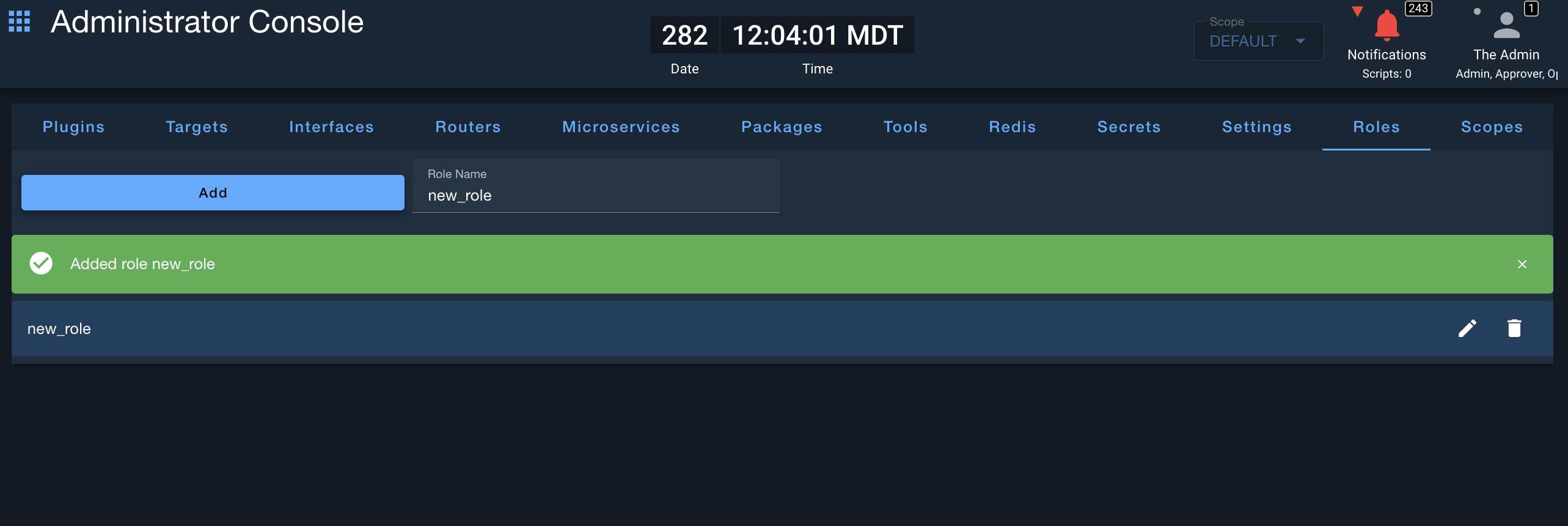
Creating Custom Roles
Custom roles are managed through the Admin Tool:
- Navigate to the Admin Tool
- Go to the Roles tab
- Click "Add" and enter a role name (single lowercase word recommended)
- Click "Edit" to configure permissions for the role
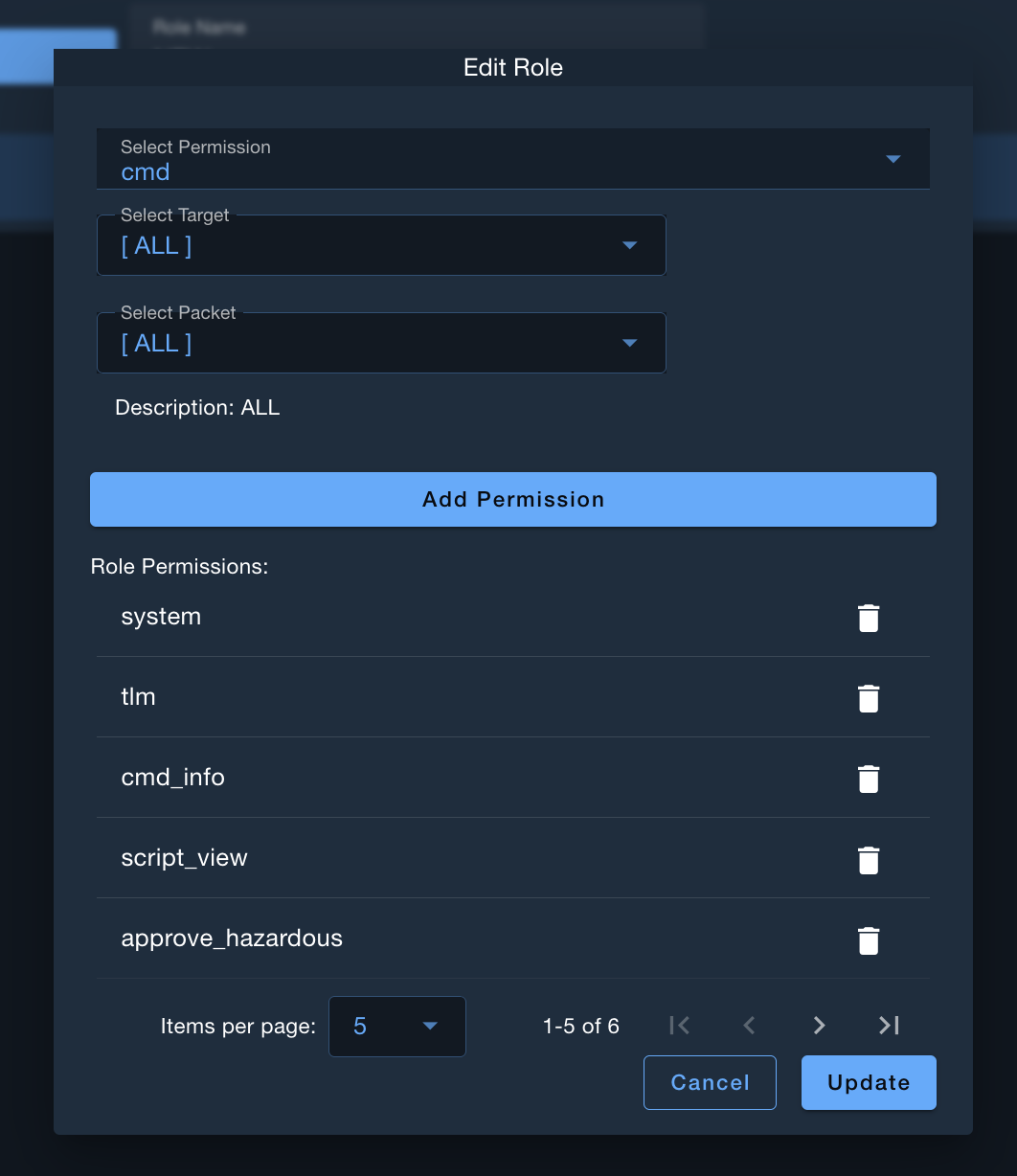
Custom Role Permissions
Custom roles can have granular permissions that target specific resources:
- target_name - Restrict permission to a specific target
- packet_name - Restrict permission to a specific packet
- interface_name - Restrict permission to a specific interface
- router_name - Restrict permission to a specific router
Example: A custom role could allow cmd permission only for the INST1 target.
Authorization Flow
When a user attempts an action, COSMOS Enterprise performs the following checks:
- Token Validation - Verify the JWT token from Keycloak
- Role Extraction - Extract roles from the token's
realm_accessclaim - Scope Matching - Match user roles against the requested scope or
ALLSCOPES - Permission Check - Verify the action's required permission is granted by the role
- Resource Matching - For custom roles, check if specific resources match
- Command Authority - If applicable, verify command authority for the target
Default Users
COSMOS Enterprise Keycloak realm includes default test users for each role:
| Username | Password | Default Role | |
|---|---|---|---|
| operator | operator | DEFAULT__operator | operator@openc3.com |
| runner | runner | DEFAULT__runner | runner@openc3.com |
| viewer | viewer | DEFAULT__viewer | viewer@openc3.com |
| admin | admin | ALLSCOPES__admin | admin@openc3.com |
| approver | approver | DEFAULT__approver | approver@openc3.com |
Note: These are default development/testing accounts. In production deployments, you should configure proper authentication and remove or change these default credentials.
Best Practices
- Principle of Least Privilege - Assign users the minimum permissions needed for their role
- Use Scopes - Leverage scopes to separate different missions or projects
- Custom Roles - Create custom roles for specialized needs rather than giving admin access
- Command Authority - Enable command authority for production systems to prevent conflicts
- Regular Audits - Review user roles and permissions periodically
- Production Security - Replace default credentials and integrate with your organization's SSO/IdP
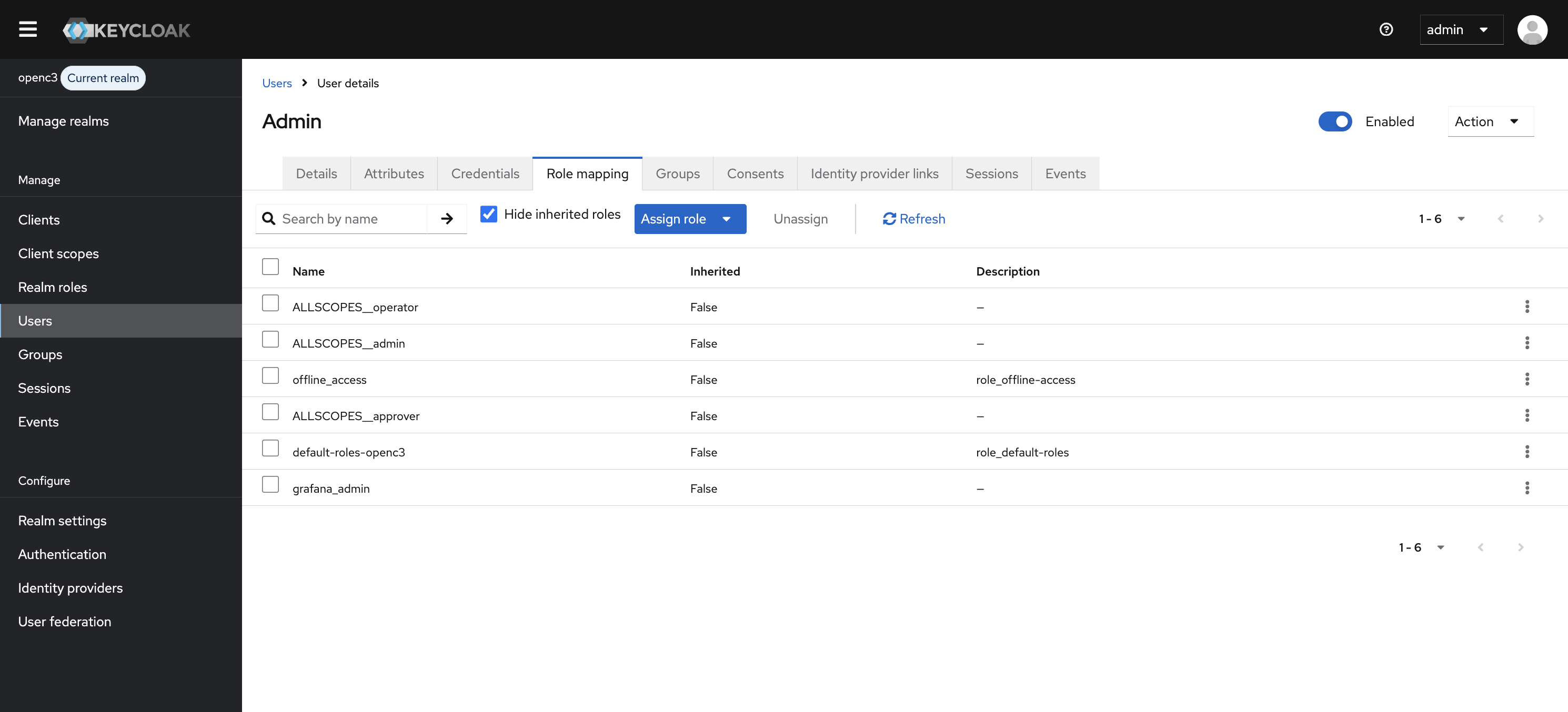
Managing Roles
Viewing / Assigning Roles to Users
Roles are managed in Keycloak:
- Access the Keycloak admin console
- Navigate to Users
- Select a user
- Go to Role Mappings
- Assign roles using the
{SCOPE}__{ROLE_NAME}format
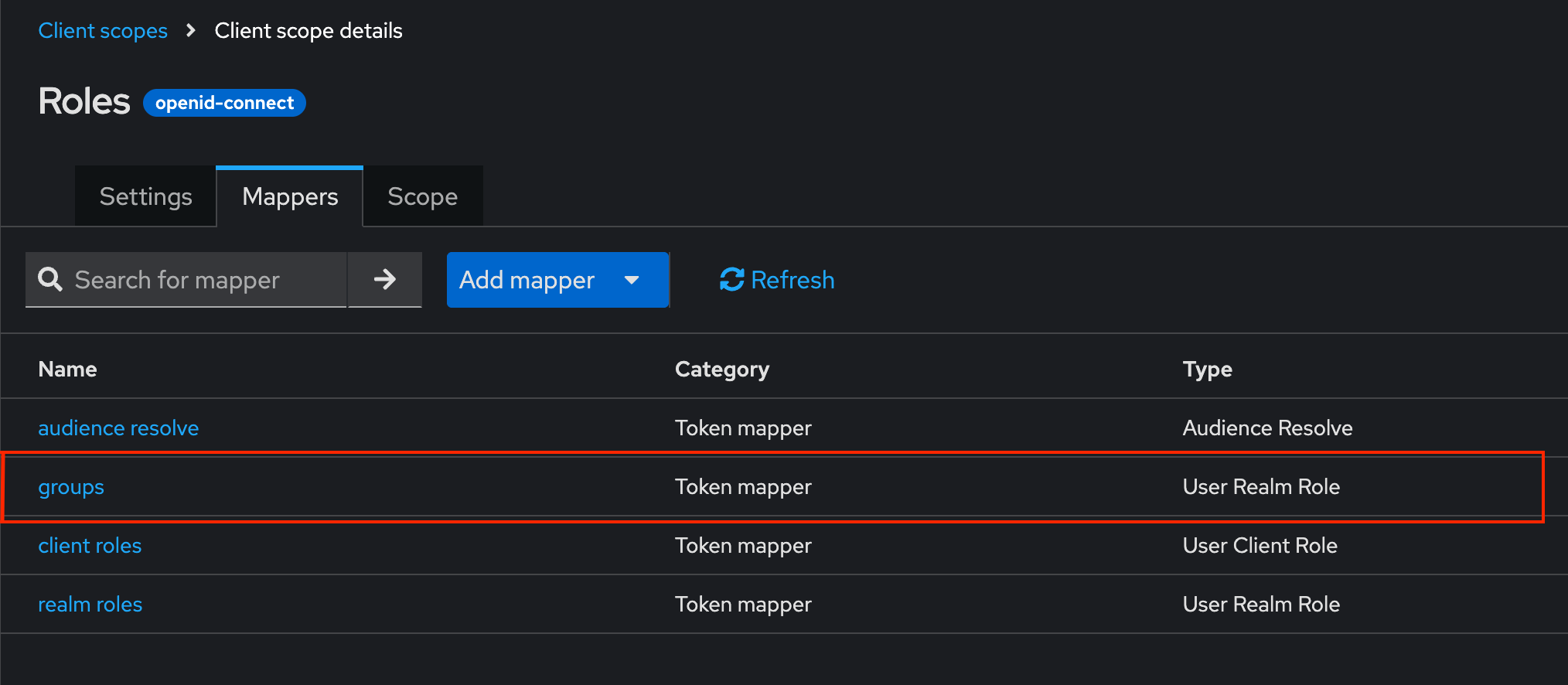
User Group Role from LDAP Federation
If you have instead imported user groups from an LDAP user federation system, you can instead assign roles to user groups rather than individual users, but you must do the following:
- Navigate to "Client Scopes"
- Click on the "roles" scope
- Go to the "Mappers" tab
- Click "Add mapper" then "From predefined mappers"
- Search for "groups" and check the box next to that, then click "Add"