Commands
Command Concepts
The COSMOS front end provides multiple ways to send commands. They can come from a script (e.g. in Script Runner), a tool like Command Sender, or just generally through an API call. These requests will go to the CmdTlmApi Server to start the flow through the rest of the COSMOS architecture and out to the target as follows:
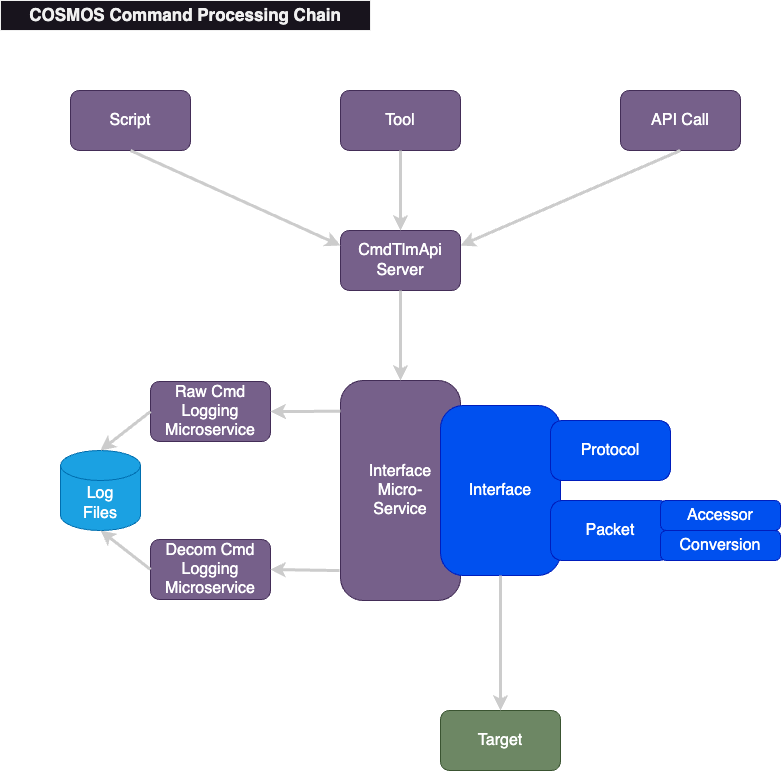
Command Definition Files
Command definition files define the command packets that can be sent to COSMOS targets. One large file can be used to define the command packets, or multiple files can be used at the user's discretion. Command definition files are placed in the target's cmd_tlm directory and are processed alphabetically. Therefore if you have some command files that depend on others, e.g. they override or extend existing commands, they must be named last. The easiest way to do this is to add an extension to an existing file name. For example, if you already have cmd.txt you can create cmd_override.txt for commands that depends on the definitions in cmd.txt. Also note that due to the way the ASCII Table is structured, files beginning with capital letters are processed before lower case letters.
When defining command parameters you can choose from the following data types: INT, UINT, FLOAT, STRING, BLOCK. These correspond to integers, unsigned integers, floating point numbers, strings and binary blocks of data. The only difference between a STRING and BLOCK is when COSMOS reads the binary command log it stops reading a STRING type when it encounters a null byte (0). This shows up in the text log produced by Data Extractor. Note that this does NOT affect the data COSMOS writes as it's still legal to pass null bytes (0) in STRING parameters. Additional data types of BOOL, ARRAY, OBJECT, and ANY are also available if you are using an Accessor that supports them. These are Booleans (true/false), arrays of unknown data type, objects with unknown contents, and a completely unknown data type with ANY.
Naming Convention
Command Packets and Parameters can be named however you want with very few exceptions. The following is not allowed in Command or Parameter names: __ (double underscore), [[ or ]] (double brackets), whitespace, and ending a name with underscore. While not much else is explicitly restricted we've found the following guidelines to be helpful.
-
Use underscores
Command names like
FIRE_THRUSTERorSET_MODEare easy to read and understand. Most parameter names can be a single word likeTYPE,DURATION, orMODEbecause they are unique within each Command. -
Be descriptive but succinct
A command name like
BUS_FLIGHT_SOFTWARE_ADCS_FIRE_THRUSTER_2is a valid command name but makes all the drop downs extra long and is a lot to type. A better choice might beFIRE_THRUSTER with POD 2. Parameters are a great way to break up complex commands. -
Avoid brackets in commands and parameters
Array items use brackets to allow indexing into an individual item. Thus if you use brackets in parameter names it gets confusing as to whether this is a COSMOS ARRAY_PARAMETER or simply a name with brackets. We support brackets for legacy reasons but avoid them when possible. For example from the Demo:
INST ARYCMD with ARRAY [1, 2, 3, 4].
Command Authority (Enterprise)
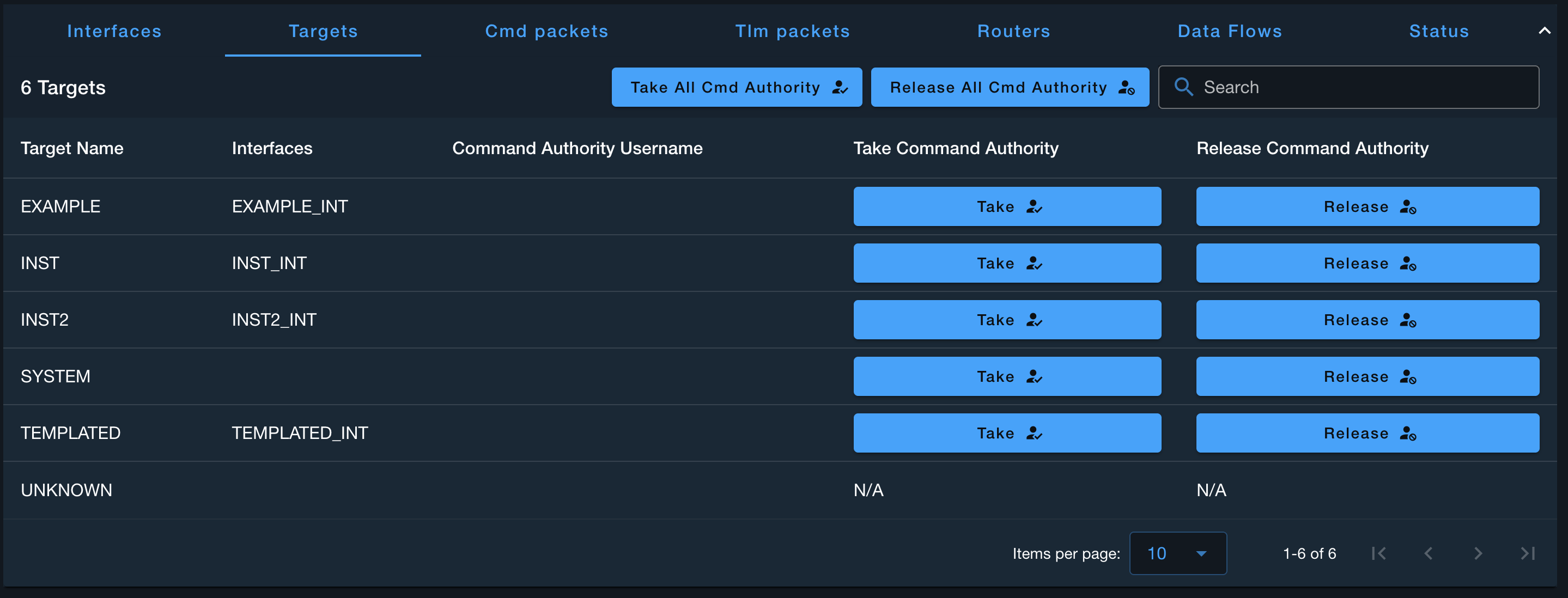
Command Authority can be enabled in the Admin Console under the Scopes tab and is enabled scope wide. Once Command Authority is enabled, individual users can take and release Command Authority which enables exclusive command and script access to that target for that user. Without taking Command Authority, users can not send a command or start a script under that target. Note, commands or scripts scheduled with Calendar or Autonomic are not affected by Command Authority.
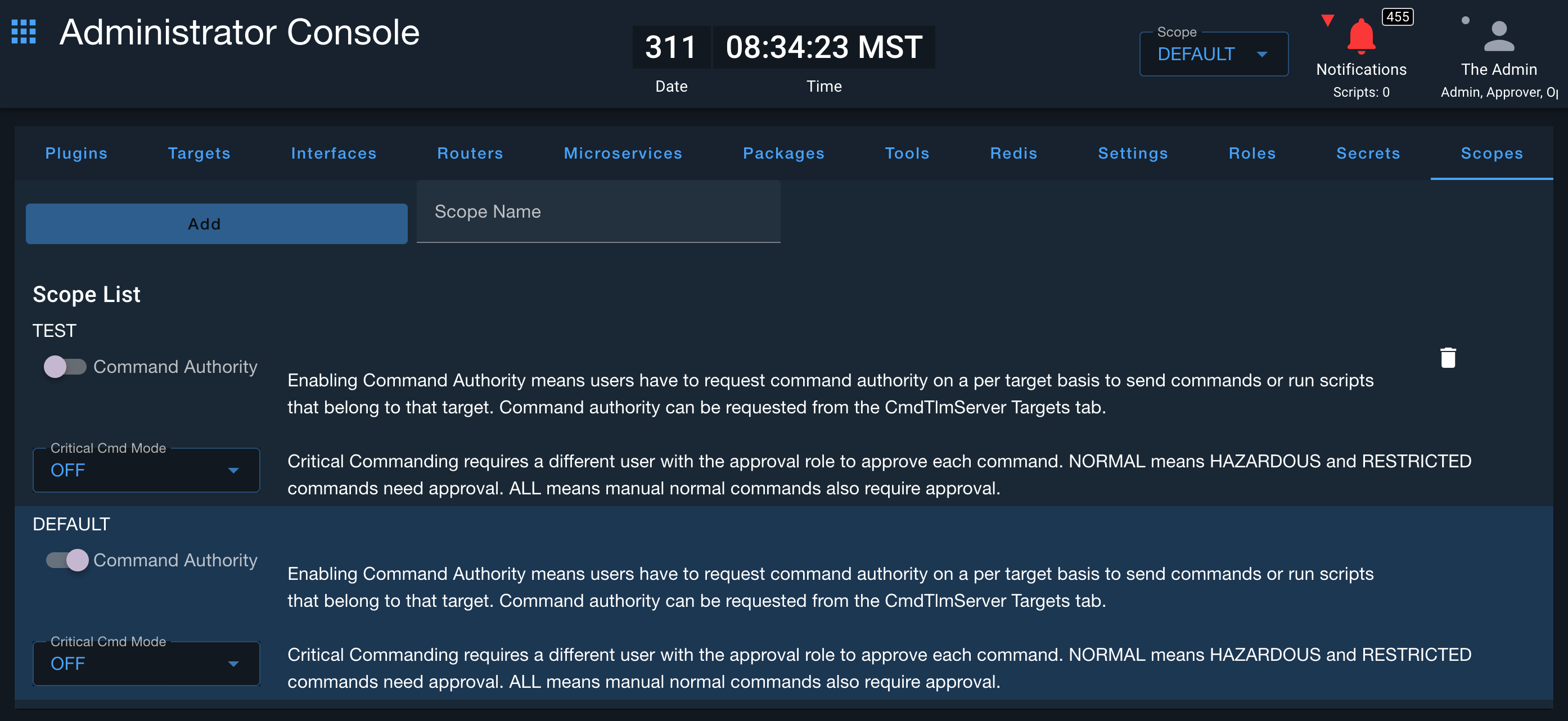
Critical Commanding (Enterprise)
Critical Commanding can be enabled in the Admin Console under the Scopes tab and is enabled scope wide. Critical commanding requires a different user to approve critical commands. When Critical Commanding mode is set to NORMAL, HAZARDOUS and RESTRICTED commands need approval. When Critical Commanding mode is set to ALL, all manual commands will require approval. OFF is the default, and disables Critical Commanding.
Here is an example of sending a HAZARDOUS command in Command Sender when Critical Command Mode is set to NORMAL.
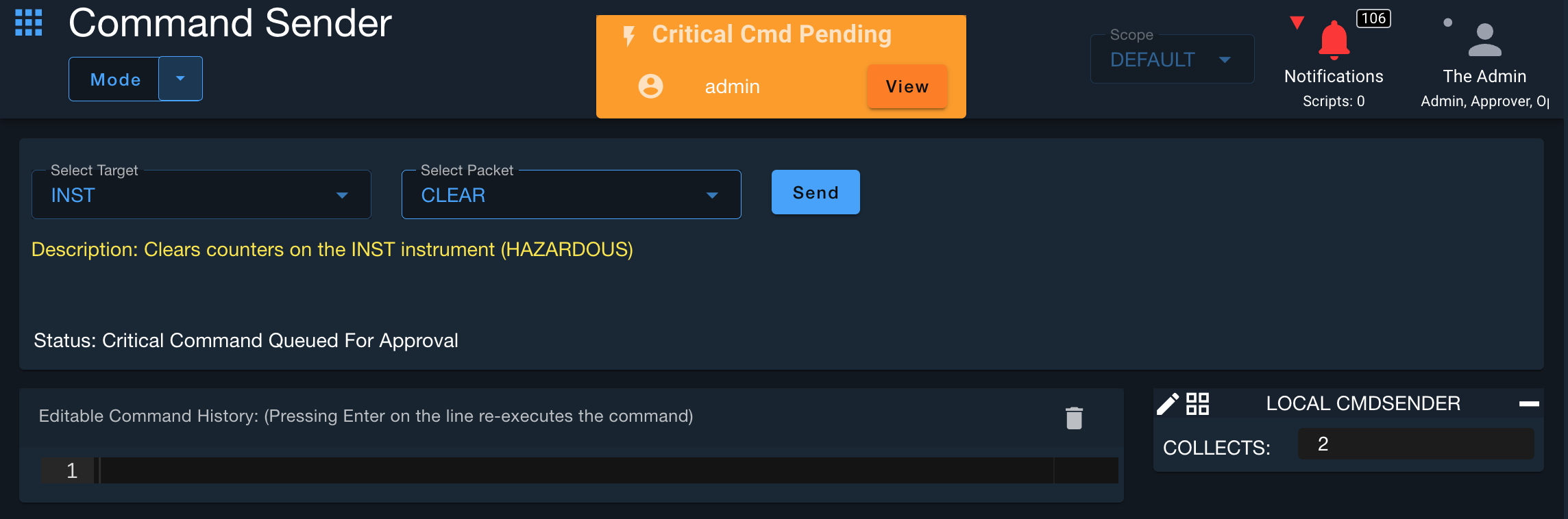
Command Keywords
COMMAND
Defines a new command packet
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Target | Name of the target this command is associated with | True |
| Command | Name of this command. Also referred to as its mnemonic. Must be unique to commands to this target. Ideally will be as short and clear as possible. | True |
| Endianness | Indicates if the data in this command is to be sent in Big Endian or Little Endian format Valid Values: BIG_ENDIAN, LITTLE_ENDIAN | True |
| Description | Description of this command which must be enclosed with quotes | False |
Example Usage:
COMMAND INST COLLECT BIG_ENDIAN "Start collect"
COMMAND Modifiers
The following keywords must follow a COMMAND keyword.
PARAMETER
Defines a command parameter in the current command packet
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Name | Name of the parameter. Must be unique within the command. | True |
| Bit Offset | Bit offset into the command packet of the Most Significant Bit of this parameter. May be negative to indicate an offset from the end of the packet. Always use a bit offset of 0 for derived parameters. | True |
| Bit Size | Bit size of this parameter. Zero or Negative values may be used to indicate that a string fills the packet up to the offset from the end of the packet specified by this value. If Bit Offset is 0 and Bit Size is 0 then this is a derived parameter and the Data Type must be set to 'DERIVED'. | True |
| Data Type | Data Type of this parameter Valid Values: INT, UINT, FLOAT, DERIVED, STRING, BLOCK | True |
When Data Type is INT, UINT, FLOAT, DERIVED the remaining parameters are:
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Minimum Value | Minimum allowed value for this parameter | True |
| Maximum Value | Maximum allowed value for this parameter | True |
| Default Value | Default value for this parameter. You must provide a default but if you mark the parameter REQUIRED then scripts will be forced to specify a value. | True |
| Description | Description for this parameter which must be enclosed with quotes | False |
| Endianness | Indicates if the data in this command is to be sent in Big Endian or Little Endian format. See guide on Little Endian Bitfields. Valid Values: BIG_ENDIAN, LITTLE_ENDIAN | False |
When Data Type is STRING, BLOCK the remaining parameters are:
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Default Value | Default value for this parameter. You must provide a default but if you mark the parameter REQUIRED then scripts will be forced to specify a value. | True |
| Description | Description for this parameter which must be enclosed with quotes | False |
| Endianness | Indicates if the data in this command is to be sent in Big Endian or Little Endian format Valid Values: BIG_ENDIAN, LITTLE_ENDIAN | False |
Example Usage:
PARAMETER SYNC 0 32 UINT 0xDEADBEEF 0xDEADBEEF 0xDEADBEEF "Sync pattern"
PARAMETER DATA 32 32 INT MIN MAX 0 "Data value"
PARAMETER VALUE 64 32 FLOAT 0 10.5 2.5
PARAMETER LABEL 96 96 STRING "OPENC3" "The label to apply"
PARAMETER BLOCK 192 0 BLOCK 0x0 "Block of binary data"
PARAMETER Modifiers
The following keywords must follow a PARAMETER keyword.
FORMAT_STRING
Adds printf style formatting
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Format | How to format using printf syntax. For example, '0x%0X' will display the value in hex. | True |
Example Usage:
FORMAT_STRING "0x%0X"
UNITS
Add displayed units
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Full Name | Full name of the units type, e.g. Celsius | True |
| Abbreviated | Abbreviation for the units, e.g. C | True |
Example Usage:
UNITS Celsius C
UNITS Kilometers KM
DESCRIPTION
Override the defined description
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Value | The new description | True |
META
Stores custom user metadata
Meta data is user specific data that can be used by custom tools for various purposes. One example is to store additional information needed to generate source code header files.
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Meta Name | Name of the metadata to store | True |
| Meta Values | One or more values to be stored for this Meta Name | False |
Example Usage:
META TEST "This parameter is for test purposes only"
OVERLAP
Since 4.4.1This item is allowed to overlap other items in the packet
If an item's bit offset overlaps another item, OpenC3 issues a warning. This keyword explicitly allows an item to overlap another and suppresses the warning message.
KEY
Since 5.0.10Defines the key used to access this raw value in the packet.
Keys are often JSONPath or XPath strings
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Key string | The key to access this item | True |
Example Usage:
KEY $.book.title
VARIABLE_BIT_SIZE
Since 5.18.0Marks an item as having its bit size defined by another length item
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Length Item Name | The name of the associated length item | True |
| Length Bits Per Count | Bits per count of the length item. Defaults to 8 | False |
| Length Value Bit Offset | Offset in Bits to Apply to Length Field Value. Defaults to 0 | False |
OBFUSCATE
Since 6.6.0Hides the item value in the UI, text logs, and raw binary file
REQUIRED
Parameter is required to be populated in scripts
When sending the command via Script Runner a value must always be given for the current command parameter. This prevents the user from relying on a default value. Note that this does not affect Command Sender which will still populate the field with the default value provided in the PARAMETER definition.
MINIMUM_VALUE
Override the defined minimum value
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Value | The new minimum value for the parameter | True |
MAXIMUM_VALUE
Override the defined maximum value
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Value | The new maximum value for the parameter | True |
DEFAULT_VALUE
Override the defined default value
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Value | The new default value for the parameter | True |
STATE
Defines a key/value pair for the current command parameter
Key value pairs allow for user friendly strings. For example, you might define states for ON = 1 and OFF = 0. This allows the word ON to be used rather than the number 1 when sending the command parameter and allows for much greater clarity and less chance for user error.
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Key | The string state name | True |
| Value | The numerical state value | True |
| Hazardous / Disable Messages | Indicates the state is hazardous. This will cause a popup to ask for user confirmation when sending this command. For non-hazardous states you can also set DISABLE_MESSAGES which will not print the command when using that state. Valid Values: HAZARDOUS | False |
| Hazardous Description | String describing why this state is hazardous | False |
Example Usage:
APPEND_PARAMETER ENABLE 32 UINT 0 1 0 "Enable setting"
STATE FALSE 0
STATE TRUE 1
APPEND_PARAMETER STRING 1024 STRING "NOOP" "String parameter"
STATE "NOOP" "NOOP" DISABLE_MESSAGES
STATE "ARM LASER" "ARM LASER" HAZARDOUS "Arming the laser is an eye safety hazard"
STATE "FIRE LASER" "FIRE LASER" HAZARDOUS "WARNING! Laser will be fired!"
WRITE_CONVERSION
Applies a conversion when writing the current command parameter
Conversions are implemented in a custom Ruby or Python file which should be
located in the target's lib folder. The class must inherit from Conversion.
It must implement the initialize (Ruby) or __init__ (Python) method if it
takes extra parameters and must always implement the call method. The conversion
factor is applied to the value entered by the user before it is written into
the binary command packet and sent. For more information see the Conversion documentation.
When applying a write_conversion sometimes the data type changes, e.g. creating a UINT from an input STRING (for an example of this see ip_write_conversion.rb or ip_write_conversion.py). In this case, the command definition data type is UINT and the min, max values don't matter (but must be given) so are typically set to MIN MAX. The default value is important and should be specified as a string. For a full example see the IP_ADDRESS parameter in the TIME_OFFSET command definition of the COSMOS Demo INST inst_cmds.txt or INST2 inst_cmds.txt.
When a command is built, each item gets written (and write conversions are run) to set the default value. Then items are written (again write conversions are run) with user provided values. Thus write conversions can be run twice. Also there are no guarantees which parameters have already been written. The packet itself has a given_values() method which can be used to retrieve a hash of the user provided values to the command. That can be used to check parameter values passed in.
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Class Filename | The filename which contains the Ruby or Python class. The filename must be named after the class such that the class is a CamelCase version of the underscored filename. For example, 'the_great_conversion.rb' should contain 'class TheGreatConversion'. Note the built-in Python conversions must specify the full path to the file, e.g. 'openc3/conversions/bit_reverse_conversion.py'. | True |
| Parameter | Additional parameter values for the conversion which are passed to the class constructor. | False |
- Python
- Ruby
WRITE_CONVERSION openc3/conversions/ip_write_conversion.py
WRITE_CONVERSION ip_write_conversion.rb
POLY_WRITE_CONVERSION
Adds a polynomial conversion factor to the current command parameter
See Polynomial Conversion for more information.
SEG_POLY_WRITE_CONVERSION
Adds a segmented polynomial conversion factor to the current command parameter
See Segmented Polynomial Conversion for more information.
GENERIC_WRITE_CONVERSION_START
Start a generic write conversion
Adds a generic conversion function to the current command parameter. This conversion factor is applied to the value entered by the user before it is written into the binary command packet and sent. The conversion is specified as Ruby or Python code that receives two implied parameters. 'value' which is the raw value being written and 'packet' which is a reference to the command packet class (Note, referencing the packet as 'myself' is still supported for backwards compatibility). The last line of code should return the converted value. The GENERIC_WRITE_CONVERSION_END keyword specifies that all lines of code for the conversion have been given.
When a command is built, each item gets written (and write conversions are run) to set the default value. Then items are written (again write conversions are run) with user provided values. Thus write conversions can be run twice. Also there are no guarantees which parameters have already been written. The packet itself has a given_values() method which can be used to retrieve a hash of the user provided values to the command. That can be used to check parameter values passed in.
Generic conversions are not a good long term solution. Consider creating a conversion class and using WRITE_CONVERSION instead. WRITE_CONVERSION is easier to debug and higher performance.
- Python
- Ruby
APPEND_PARAMETER ITEM1 32 UINT 0 0xFFFFFFFF 0
GENERIC_WRITE_CONVERSION_START
int(value * 1.5) # Convert the value by a scale factor
GENERIC_WRITE_CONVERSION_END
APPEND_PARAMETER ITEM1 32 UINT 0 0xFFFFFFFF 0
GENERIC_WRITE_CONVERSION_START
(value * 1.5).to_i # Convert the value by a scale factor
GENERIC_WRITE_CONVERSION_END
GENERIC_WRITE_CONVERSION_END
Complete a generic write conversion
OVERFLOW
Set the behavior when writing a value overflows the type
By default OpenC3 throws an error if you try to write a value which overflows its specified type, e.g. writing 255 to a 8 bit signed value. Setting the overflow behavior also allows for OpenC3 to 'TRUNCATE' the value by eliminating any high order bits. You can also set 'SATURATE' which causes OpenC3 to replace the value with the maximum or minimum allowable value for that type. Finally you can specify 'ERROR_ALLOW_HEX' which will allow for a maximum hex value to be written, e.g. you can successfully write 255 to a 8 bit signed value.
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Behavior | How OpenC3 treats an overflow value. Only applies to signed and unsigned integer data types. Valid Values: ERROR, ERROR_ALLOW_HEX, TRUNCATE, SATURATE | True |
Example Usage:
OVERFLOW TRUNCATE
HIDDEN
Hides this parameter from all the OpenC3 tools
This item will not appear in CmdSender. It also hides this item from appearing in the Script Runner popup helper when writing scripts. The parameter should not be provided to commands.
APPEND_PARAMETER
Defines a command parameter in the current command packet
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Name | Name of the parameter. Must be unique within the command. | True |
| Bit Size | Bit size of this parameter. Zero or Negative values may be used to indicate that a string fills the packet up to the offset from the end of the packet specified by this value. If Bit Offset is 0 and Bit Size is 0 then this is a derived parameter and the Data Type must be set to 'DERIVED'. | True |
| Data Type | Data Type of this parameter Valid Values: INT, UINT, FLOAT, DERIVED, STRING, BLOCK | True |
When Data Type is INT, UINT, FLOAT, DERIVED the remaining parameters are:
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Minimum Value | Minimum allowed value for this parameter | True |
| Maximum Value | Maximum allowed value for this parameter | True |
| Default Value | Default value for this parameter. You must provide a default but if you mark the parameter REQUIRED then scripts will be forced to specify a value. | True |
| Description | Description for this parameter which must be enclosed with quotes | False |
| Endianness | Indicates if the data in this command is to be sent in Big Endian or Little Endian format. See guide on Little Endian Bitfields. Valid Values: BIG_ENDIAN, LITTLE_ENDIAN | False |
When Data Type is STRING, BLOCK the remaining parameters are:
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Default Value | Default value for this parameter. You must provide a default but if you mark the parameter REQUIRED then scripts will be forced to specify a value. | True |
| Description | Description for this parameter which must be enclosed with quotes | False |
| Endianness | Indicates if the data in this command is to be sent in Big Endian or Little Endian format Valid Values: BIG_ENDIAN, LITTLE_ENDIAN | False |
Example Usage:
APPEND_PARAMETER SYNC 32 UINT 0xDEADBEEF 0xDEADBEEF 0xDEADBEEF "Sync pattern"
APPEND_PARAMETER VALUE 32 FLOAT 0 10.5 2.5
APPEND_PARAMETER LABEL 0 STRING "OPENC3" "The label to apply"
ID_PARAMETER
Defines an identification command parameter in the current command packet. Note, packets defined without one or more ID_PARAMETERs are "catch-all" packets which will match all incoming data. A warning will be generated for packets without ID_PARAMETERs unless the CATCHALL keyword is used.
ID parameters are used to identify the binary block of data as a particular command. A command packet may have one or more ID_PARAMETERs and all must match the binary data for the command to be identified.
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Name | Name of the parameter. Must be unique within the command. | True |
| Bit Offset | Bit offset into the command packet of the Most Significant Bit of this parameter. May be negative to indicate an offset from the end of the packet. | True |
| Bit Size | Bit size of this parameter. Zero or Negative values may be used to indicate that a string fills the packet up to the offset from the end of the packet specified by this value. If Bit Offset is 0 and Bit Size is 0 then this is a derived parameter and the Data Type must be set to 'DERIVED'. | True |
| Data Type | Data Type of this parameter Valid Values: INT, UINT, FLOAT, DERIVED, STRING, BLOCK | True |
When Data Type is INT, UINT, FLOAT, DERIVED the remaining parameters are:
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Minimum Value | Minimum allowed value for this parameter | True |
| Maximum Value | Maximum allowed value for this parameter | True |
| ID Value | Identification value for this parameter. The binary data must match this value for the buffer to be identified as this packet. | True |
| Description | Description for this parameter which must be enclosed with quotes | False |
| Endianness | Indicates if the data in this command is to be sent in Big Endian or Little Endian format. See guide on Little Endian Bitfields. Valid Values: BIG_ENDIAN, LITTLE_ENDIAN | False |
When Data Type is STRING, BLOCK the remaining parameters are:
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Default Value | Default value for this parameter. You must provide a default but if you mark the parameter REQUIRED then scripts will be forced to specify a value. | True |
| Description | Description for this parameter which must be enclosed with quotes | False |
| Endianness | Indicates if the data in this command is to be sent in Big Endian or Little Endian format Valid Values: BIG_ENDIAN, LITTLE_ENDIAN | False |
Example Usage:
ID_PARAMETER OPCODE 32 32 UINT 2 2 2 "Opcode identifier"
APPEND_ID_PARAMETER
Defines an identification command parameter in the current command packet
ID parameters are used to identify the binary block of data as a particular command. A command packet may have one or more ID_PARAMETERs and all must match the binary data for the command to be identified.
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Name | Name of the parameter. Must be unique within the command. | True |
| Bit Size | Bit size of this parameter. Zero or Negative values may be used to indicate that a string fills the packet up to the offset from the end of the packet specified by this value. If Bit Offset is 0 and Bit Size is 0 then this is a derived parameter and the Data Type must be set to 'DERIVED'. | True |
| Data Type | Data Type of this parameter Valid Values: INT, UINT, FLOAT, DERIVED, STRING, BLOCK | True |
When Data Type is INT, UINT, FLOAT, DERIVED the remaining parameters are:
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Minimum Value | Minimum allowed value for this parameter | True |
| Maximum Value | Maximum allowed value for this parameter | True |
| ID Value | Identification value for this parameter. The binary data must match this value for the buffer to be identified as this packet. | True |
| Description | Description for this parameter which must be enclosed with quotes | False |
| Endianness | Indicates if the data in this command is to be sent in Big Endian or Little Endian format. See guide on Little Endian Bitfields. Valid Values: BIG_ENDIAN, LITTLE_ENDIAN | False |
When Data Type is STRING, BLOCK the remaining parameters are:
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Default Value | Default value for this parameter. You must provide a default but if you mark the parameter REQUIRED then scripts will be forced to specify a value. | True |
| Description | Description for this parameter which must be enclosed with quotes | False |
| Endianness | Indicates if the data in this command is to be sent in Big Endian or Little Endian format Valid Values: BIG_ENDIAN, LITTLE_ENDIAN | False |
Example Usage:
APPEND_ID_PARAMETER OPCODE 32 UINT 2 2 2 "Opcode identifier"
ARRAY_PARAMETER
Defines a command parameter in the current command packet that is an array
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Name | Name of the parameter. Must be unique within the command. | True |
| Bit Offset | Bit offset into the command packet of the Most Significant Bit of this parameter. May be negative to indicate an offset from the end of the packet. Always use a bit offset of 0 for derived parameters. | True |
| Item Bit Size | Bit size of each array item | True |
| Item Data Type | Data Type of each array item Valid Values: INT, UINT, FLOAT, STRING, BLOCK, DERIVED | True |
| Array Bit Size | Total Bit Size of the Array. Zero or Negative values may be used to indicate the array fills the packet up to the offset from the end of the packet specified by this value. | True |
| Description | Description which must be enclosed with quotes | False |
| Endianness | Indicates if the data is to be sent in Big Endian or Little Endian format Valid Values: BIG_ENDIAN, LITTLE_ENDIAN | False |
Example Usage:
ARRAY_PARAMETER ARRAY 64 64 FLOAT 640 "Array of 10 64bit floats"
APPEND_ARRAY_PARAMETER
Defines a command parameter in the current command packet that is an array
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Name | Name of the parameter. Must be unique within the command. | True |
| Item Bit Size | Bit size of each array item | True |
| Item Data Type | Data Type of each array item Valid Values: INT, UINT, FLOAT, STRING, BLOCK, DERIVED | True |
| Array Bit Size | Total Bit Size of the Array. Zero or Negative values may be used to indicate the array fills the packet up to the offset from the end of the packet specified by this value. | True |
| Description | Description which must be enclosed with quotes | False |
| Endianness | Indicates if the data is to be sent in Big Endian or Little Endian format Valid Values: BIG_ENDIAN, LITTLE_ENDIAN | False |
Example Usage:
APPEND_ARRAY_PARAMETER ARRAY 64 FLOAT 640 "Array of 10 64bit floats"
STRUCTURE
Since 6.10.0Adds and flattens a structure (generally a virtual packet) into the current packet. The specific named item is BLOCK type and hidden.
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Name | Name of the parameter. Must be unique within the command. | True |
| Bit Offset | Bit offset into the command packet of the Most Significant Bit of this parameter. May be negative to indicate an offset from the end of the packet. Always use a bit offset of 0 for derived parameters. | True |
| Bit Size | Bit size of this parameter. Zero or Negative values may be used to indicate that a string fills the packet up to the offset from the end of the packet specified by this value. If Bit Offset is 0 and Bit Size is 0 then this is a derived parameter and the Data Type must be set to 'DERIVED'. | True |
| Command or telemetry | Whether the structure packet is a command or telemetry packet Valid Values: CMD, COMMAND, TLM, TELEMETRY | True |
| Target Name | Target Name of the structure packet | True |
| Packet Name | Packet Name of the structure packet | True |
APPEND_STRUCTURE
Since 6.10.0Adds and flattens a structure (generally a virtual packet) into the current packet. The specific named item is BLOCK type and hidden.
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Name | Name of the parameter. Must be unique within the command. | True |
| Bit Size | Bit size of this parameter. Zero or Negative values may be used to indicate that a string fills the packet up to the offset from the end of the packet specified by this value. If Bit Offset is 0 and Bit Size is 0 then this is a derived parameter and the Data Type must be set to 'DERIVED'. | True |
| Command or telemetry | Whether the structure packet is a command or telemetry packet Valid Values: CMD, COMMAND, TLM, TELEMETRY | True |
| Target Name | Target Name of the structure packet | True |
| Packet Name | Packet Name of the structure packet | True |
SELECT_PARAMETER
Selects an existing command parameter for editing
Must be used in conjunction with SELECT_COMMAND to first select the packet. Typically used to override generated values or make specific changes to commands that only affect a particular instance of a target used multiple times.
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Name of the parameter to select for modification | True |
Example Usage:
SELECT_COMMAND INST COLLECT
SELECT_PARAMETER DURATION
# Add units
UNITS Seconds S
DELETE_PARAMETER
Since 4.4.1Deletes an existing command parameter from the packet definition
Deleting a parameter from the command definition does not remove the defined space for that parameter. Thus unless you redefine a new parameter, there will be a "hole" in the packet where the data is not accessible. You can use SELECT_COMMAND and then PARAMETER to define a new parameter.
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Name of the parameter to delete | True |
Example Usage:
SELECT_COMMAND INST COLLECT
DELETE_PARAMETER DURATION
HIDDEN
Hides this command from all OpenC3 tools such as Command Sender and Handbook Creator
Hidden commands do not appear in the Script Runner popup helper when writing scripts. The command still exists in the system and can be sent by scripts.
DISABLED
Disables this command from being sent
Hides the command and also disables it from being sent by scripts. Attempts to send DISABLED commands result in an error message.
DISABLE_MESSAGES
Disable the Server from printing cmd(...) messages. Commands are still logged.
META
Stores metadata for the current command
Meta data is user specific data that can be used by custom tools for various purposes. One example is to store additional information needed to generate source code header files.
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Meta Name | Name of the metadata to store | True |
| Meta Values | One or more values to be stored for this Meta Name | False |
Example Usage:
META FSW_TYPE "struct command"
HAZARDOUS
Designates the current command as hazardous
Sending a hazardous command causes a dialog asking for confirmation before sending the command
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Description | Description for why the command is hazardous which must be enclosed with quotes | False |
ACCESSOR
Since 5.0.10Defines the class used to read and write raw values from the packet
Defines the class that is used too read raw values from the packet. Defaults to BinaryAccessor. For more information see Accessors.
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Accessor Class Name | The name of the accessor class | True |
| Argument | Additional argument passed to the accessor class constructor | False |
SUBPACKETIZER
Since 6.10.0Defines a class used to break up the packet into subpackets before decom
Defines a class used to break up the packet into subpackets before decom. Defaults to nil/None.
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Subpacketizer Class Name | The name of the Subpacketizer class | True |
| Argument | Additional argument passed to the Subpacketizer class constructor | False |
TEMPLATE
Since 5.0.10Defines a template string used to initialize the command before default values are filled in
Generally the template string is formatted in JSON or HTML and then values are filled in with command parameters. Must be UTF-8 encoded.
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Template | The template string which should be enclosed in quotes | True |
TEMPLATE_BASE64
Since 7.0.0Defines a template binary as base64 used to initialize the command before default values are filled in
Base64 encoded binary data
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Template | The template string as base64 data | True |
TEMPLATE_FILE
Since 5.0.10Defines a template file used to initialize the command before default values are filled in
Generally the template file is formatted in JSON or HTML and then values are filled in with command parameters. Can be binary or UTF-8.
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Template File Path | The relative path to the template file. Filename should generally start with an underscore. | True |
RESPONSE
Since 5.14.0Indicates the expected telemetry packet response to this command
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Target Name | Target Name of telemetry response packet | True |
| Packet Name | Packet Name of telemetry response packet | True |
ERROR_RESPONSE
Since 5.14.0Indicates the expected telemetry packet error response to this command
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Target Name | Target Name of telemetry error response packet | True |
| Packet Name | Packet Name of telemetry error response packet | True |
RELATED_ITEM
Since 5.14.0Defines a related telemetry item to this command
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Target Name | Target Name of related telemetry item | True |
| Packet Name | Packet Name of related telemetry item | True |
| Item Name | Item Name of related telemetry item | True |
SCREEN
Since 5.14.0Defines a related telemetry screen to this command
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Target Name | Target Name of related telemetry screen | True |
| Screen Name | Screen Name of related telemetry screen | True |
CATCHALL
Since 7.0.0Marks this packet as an intentional catch-all packet
Suppresses the warning that is normally generated for packets defined without ID_PARAMETERs. Use this when a packet is intentionally designed to match all incoming data that doesn't match other packets.
VIRTUAL
Since 5.18.0Marks this packet as virtual and not participating in identification
Used for packet definitions that can be used as structures for items with a given packet.
RESTRICTED
Since 5.20.0Marks this packet as restricted and will require approval if critical commanding is enabled
Used as one of the two types of critical commands (HAZARDOUS and RESTRICTED)
SUBPACKET
Since 6.10.0Marks this packet as as a subpacket which will exclude it from Interface level identification
Used with a SUBPACKETIZER to breakup up packets into subpackets at decom time
VALIDATOR
Since 5.19.0Defines a validator class for a command
Validator class is used to validate the command success or failure with both a pre_check and post_check method.
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Class Filename | The filename which contains the Ruby or Python class. The filename must be named after the class such that the class is a CamelCase version of the underscored filename. For example, 'command_validator.rb' should contain 'class CommandValidator'. | True |
| Argument | Additional argument passed to the validator class constructor | False |
- Python
- Ruby
VALIDATOR custom_validator.py
Defined in custom_validator.py:
class CustomValidator(CommandValidator):
# Both the pre_check and post_check are passed the command packet that was sent
# You can inspect the command in your checks as follows:
# packet.target_name => target name
# packet.packet_name => packet name (command name)
# packet.read("ITEM") => converted value
# packet.read("ITEM", :RAW) => raw value
def pre_check(self, command):
if tlm("TGT PKT ITEM") == 0:
return [False, "TGT PKT ITEM is 0"]
self.cmd_acpt_cnt = tlm("INST HEALTH_STATUS CMD_ACPT_CNT")
# Return true to indicate Success, false to indicate Failure,
# and nil to indicate Unknown. The second value is the optional message.
return [True, None]
def post_check(self, command):
wait_check(f"INST HEALTH_STATUS CMD_ACPT_CNT > {self.cmd_acpt_cnt}", 10)
# Return true to indicate Success, false to indicate Failure,
# and nil to indicate Unknown. The second value is the optional message.
return [True, None]
VALIDATOR custom_validator.rb
Defined in custom_validator.rb:
require 'openc3/packets/command_validator'
class CustomValidator < OpenC3::CommandValidator
# Both the pre_check and post_check are passed the command packet that was sent
# You can inspect the command in your checks as follows:
# packet.target_name => target name
# packet.packet_name => packet name (command name)
# packet.read("ITEM") => converted value
# packet.read("ITEM", :RAW) => raw value
def pre_check(packet)
if tlm("TGT PKT ITEM") == 0
return [false, "TGT PKT ITEM is 0"]
end
@cmd_acpt_cnt = tlm("TGT PKT CMD_ACPT_CNT")
# Return true to indicate Success, false to indicate Failure,
# and nil to indicate Unknown. The second value is the optional message.
return [true, nil]
end
def post_check(packet)
wait_check("TGT PKT CMD_ACPT_CNT > #{@cmd_acpt_cnt}", 10)
# Return true to indicate Success, false to indicate Failure,
# and nil to indicate Unknown. The second value is the optional message.
return [true, nil]
end
end
SELECT_COMMAND
Selects an existing command packet for editing
Typically used in a separate configuration file from where the original command is defined to override or add to the existing command definition. Must be used in conjunction with SELECT_PARAMETER to change an individual parameter.
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Target Name | Name of the target this command is associated with | True |
| Command Name | Name of the command to select | True |
Example Usage:
SELECT_COMMAND INST COLLECT
SELECT_PARAMETER DURATION
# Add units
UNITS Seconds S
Example File
Example File: TARGET/cmd_tlm/cmd.txt
COMMAND TARGET COLLECT_DATA BIG_ENDIAN "Commands my target to collect data"
PARAMETER CCSDSVER 0 3 UINT 0 0 0 "CCSDS PRIMARY HEADER VERSION NUMBER"
PARAMETER CCSDSTYPE 3 1 UINT 1 1 1 "CCSDS PRIMARY HEADER PACKET TYPE"
PARAMETER CCSDSSHF 4 1 UINT 0 0 0 "CCSDS PRIMARY HEADER SECONDARY HEADER FLAG"
ID_PARAMETER CCSDSAPID 5 11 UINT 0 2047 100 "CCSDS PRIMARY HEADER APPLICATION ID"
PARAMETER CCSDSSEQFLAGS 16 2 UINT 3 3 3 "CCSDS PRIMARY HEADER SEQUENCE FLAGS"
PARAMETER CCSDSSEQCNT 18 14 UINT 0 16383 0 "CCSDS PRIMARY HEADER SEQUENCE COUNT"
PARAMETER CCSDSLENGTH 32 16 UINT 4 4 4 "CCSDS PRIMARY HEADER PACKET LENGTH"
PARAMETER ANGLE 48 32 FLOAT -180.0 180.0 0.0 "ANGLE OF INSTRUMENT IN DEGREES"
POLY_WRITE_CONVERSION 0 0.01745 0 0
PARAMETER MODE 80 8 UINT 0 1 0 "DATA COLLECTION MODE"
STATE NORMAL 0
STATE DIAG 1
COMMAND TARGET NOOP BIG_ENDIAN "Do Nothing"
PARAMETER CCSDSVER 0 3 UINT 0 0 0 "CCSDS PRIMARY HEADER VERSION NUMBER"
PARAMETER CCSDSTYPE 3 1 UINT 1 1 1 "CCSDS PRIMARY HEADER PACKET TYPE"
PARAMETER CCSDSSHF 4 1 UINT 0 0 0 "CCSDS PRIMARY HEADER SECONDARY HEADER FLAG"
ID_PARAMETER CCSDSAPID 5 11 UINT 0 2047 101 "CCSDS PRIMARY HEADER APPLICATION ID"
PARAMETER CCSDSSEQFLAGS 16 2 UINT 3 3 3 "CCSDS PRIMARY HEADER SEQUENCE FLAGS"
PARAMETER CCSDSSEQCNT 18 14 UINT 0 16383 0 "CCSDS PRIMARY HEADER SEQUENCE COUNT"
PARAMETER CCSDSLENGTH 32 16 UINT 0 0 0 "CCSDS PRIMARY HEADER PACKET LENGTH"
PARAMETER DUMMY 48 8 UINT 0 0 0 "DUMMY PARAMETER BECAUSE CCSDS REQUIRES 1 BYTE OF DATA"
COMMAND TARGET SETTINGS BIG_ENDIAN "Set the Settings"
PARAMETER CCSDSVER 0 3 UINT 0 0 0 "CCSDS PRIMARY HEADER VERSION NUMBER"
PARAMETER CCSDSTYPE 3 1 UINT 1 1 1 "CCSDS PRIMARY HEADER PACKET TYPE"
PARAMETER CCSDSSHF 4 1 UINT 0 0 0 "CCSDS PRIMARY HEADER SECONDARY HEADER FLAG"
ID_PARAMETER CCSDSAPID 5 11 UINT 0 2047 102 "CCSDS PRIMARY HEADER APPLICATION ID"
PARAMETER CCSDSSEQFLAGS 16 2 UINT 3 3 3 "CCSDS PRIMARY HEADER SEQUENCE FLAGS"
PARAMETER CCSDSSEQCNT 18 14 UINT 0 16383 0 "CCSDS PRIMARY HEADER SEQUENCE COUNT"
PARAMETER CCSDSLENGTH 32 16 UINT 0 0 0 "CCSDS PRIMARY HEADER PACKET LENGTH"
<% 5.times do |x| %>
APPEND_PARAMETER SETTING<%= x %> 16 UINT 0 5 0 "Setting <%= x %>"
<% end %>